When it comes to selecting wheelchairs for seniors, there is no one-size-fits-all solution, which is why it can be challenging to find the perfect fit! While you may occasionally use stock wheelchairs for short-term transportation, residents who spend most of their time in a wheelchair need seating customized to their unique bodies.
How to Select a Wheelchair
- Determine the right type of wheelchair
- Size your wheelchair properly
- Select the appropriate features
To a healthy person, sitting in an awkward position is uncomfortable, but for seniors it can be a danger to their health. The first step to finding the correct wheelchair is to select the type of wheelchair your resident is best suited for – a decision largely dependent on the individual resident and how the wheelchair will be used.
What Are the Different Types of Wheelchairs?
Transport Wheelchairs
Transport wheelchairs feature a light and portable frame with smaller rear wheels for portability. They are designed for short-term transportation and must be propelled by a caregiver or other individual.
Lightweight Wheelchairs
Lightweight wheelchairs are easy to fold and transport, and often feature removable and adjustable components to assist in accessibility.

Standard Wheelchairs
Standard wheelchairs are the most common type of wheelchair, providing durable construction and high weight capacities. They are more durable than lightweight wheelchairs and generally less expensive, but not as adjustable.
Heavy Duty Wheelchairs
Heavy Duty wheelchairs offer a large-capacity reinforced frame for supreme durability.
Reclining Wheelchairs or Tilt Wheelchairs
Reclining wheelchairs and tilt wheelchairs provide pressure redistribution for resident-specific support or relief for a range of conditions. These chairs are often part of an individualized care plan based on clinical assessments.
Bariatric Wheelchairs
Bariatric Wheelchairs are the strongest type of wheelchairs, with reinforced steel at all weight-bearing points help provide additional strength. These chairs are available in wider sizes and with higher weight capacities than Heavy-Duty wheelchairs.
How to Choose a Wheelchair Size
The most important measurements you need to take are seat width, back height, seat depth and seat-to-floor height. By providing a wheelchair with the proper dimensions in these four areas, you will avoid some of the most common and dangerous positioning concerns. Measuring all fields will help ensure optimal comfort and safety.
How to Calculate a Resident’s Seat Width
- Measure the resident’s hip width across the widest point of hips or thighs
- Add 1″
- Add thickness of side cushions (if a cushion is used)
How to Calculate a Resident’s Back Height
- Measure the resident’s buttocks to underside of extended arm
- Add half the thickness of seat cushion (if used)
- Subtract 4″ for residents with good trunk muscles
- Subtract 3″ for residents with poor trunk muscles
How to Calculate a Resident’s Seat Depth
- Measure resident’s rear of buttocks to back of knee
- Subtract 2½”
- Add thickness of back cushion (if a cushion is used)
How to Determine Seat-to-Floor Height
- If resident is under 5′5″ tall, use a Hemi size wheelchair with a 17½” seat height
- If resident is between 5′5″ and 6′2″, use an Adult size wheelchair with a 19½” to 20½” seat height
- If resident is over 6′2″ tall, use a Tall size wheelchair with a 21½” seat height
Seat Width
Seat Depth
Back Height
Seat-to-Floor Height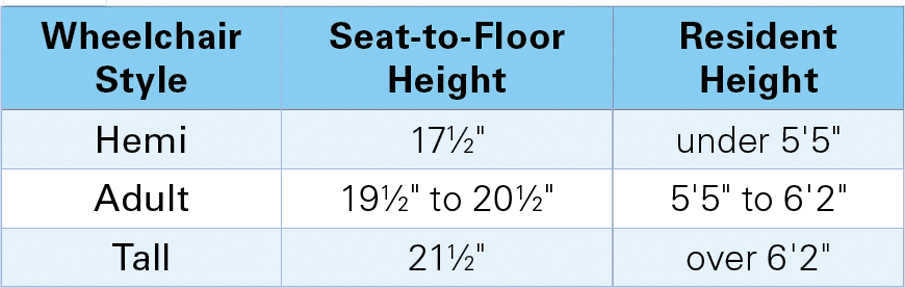
Wheelchair Features FAQ
Discover the right features to address your resident’s risk factors, activity level and acuity.
What are the different types of wheelchairs?
There are many different types of patient wheelchairs: transport wheelchairs, lightweight wheelchairs, standard wheelchairs, heavy-duty wheelchairs, bariatric wheelchairs and reclining wheelchairs. Depending on your wheelchair, learn how to select the best wheelchair cushions.
What are my options for wheelchair armrests?
Full-length armrests provide more support for easier ingress and egress while desk-length options allow the chair to fit easily under most desks or tables. Adjustable and flipback armrests can be raised and lowered to better suit the resident.
What are front riggings, and which does my resident need?
Front riggings are optional front-mounted hardware that provides a place for residents to put their feet. Swingaway footrests support the residents’ feet while they are in the chair and rotate out of the way for easier transfers. Elevating legrests support the legs with comfortable calf pads and allow angle-of-elevation adjustment. Articulating legrests are similar to elevating options, but they extend during elevation for enhanced comfort.
What are my upholstery options, and how are they different?
Vinyl is easier to clean and more durable, while nylon is lighter weight and more breathable.
What does “dual axle” mean?
Dual-axle capabilities mean that your wheelchair can transform from standard to hemi height. Hemi height is about 2″ lower than standard seating. This allows the user to more easily self-propel and is also beneficial for residents shorter than 5′ tall.
Finding the right wheelchair is one of the most important things you can do for your residents. It’s also important to remember that a wheelchair is not a singular product solution – it is part of a larger seating system. It is in combination with cushions, backrests and positioners that a wheelchair becomes a safe and comfortable solution for your residents. Learn how to choose the right cushion »
Explore our interactive wheelchair selection tool, download our in-depth guide or shop online to find the perfect wheelchair and start improving the seating systems in your community.



